Apache, otherwise known as Apache HTTP Server, is an established standard in the online distribution of website services, which gave the initial boost for the expansion of the World Wide Web. It is an open-source web server platform, which guarantees the online availability of the majority of the websites active today. The server is aimed at serving a great deal of widely popular modern web platforms/operating systems such as Unix, Windows, Linux, Solaris, Novell NetWare, FreeBSD, Mac OS X, Microsoft Windows, OS/2, etc.
There are two popular versions for the origin of the project’s name. According to the more widespread one – the web server’s name was chosen out of respect for the Native American Indian Apache tribe, well known for its resilience and military skills. The other version refers to the set of patches attached to the codebase of NCSA HTTPd 1.3, which makes it “a patchy” server.
The Apache server has been developed by an open source community – Apache Software Foundation, whose members are constantly adding new useful functionalities, with the sole purpose of providing a secure and extensible server platform that ensures HTTP service delivery in accordance with the current HTTP standards.
There is a great amount of modules created especially for the Apache server, which support various scripts and allow dynamic content to be run on the server. Most of the modules come as part of the Apache distribution, making the server boast a wide range of capabilities, such as support for CGI (Common Gateway Interface), a standard protocol for communication between external application software and a web server, and also SSI (Server Side Includes), a simple server-side scripting language. Other Apache modules include: CGI scripts execution, user authentication, URL redirection, anonymous user access, automatic directory listings, support for HTTP header metafiles, support for loading modules, content negotiation, caching proxy abilities, server status display, user home directories, etc. Users can choose to install those modules with the Apache server installation. If not, they can install them later with the help of dynamic modules.
The Apache server has been the most popular web server on the Internet since April 1996. It is by no means considered a platform criterion for the development and evaluation of other successful web servers.
Apache Server Versions
Since its initial launch the web server has undergone a number of improvements, which led to the release of several versions. All of the versions are accompanied by comprehensive documentation archives.
Apache 1.3
Apache 1.3 boasts a great deal of improvements over 1.2, the most noteworthy of them being – useful configurable files, Windows and Novell NetWare support, DSO support, APXS tool and others.
Apache 2.0 differs from the previous versions by the much re-written code, which has considerably simplified its configuration and boosted its efficiency. It supports Ipv6, Unix threading, other protocols such as mod_echo. This version also offers a new compilation system and multi-language error messaging.
Apache 2.2 came out in 2006 and offers new and more flexible modules for user authentication and proxy caching, support for files exceeding 2 GB, as well as SQL support.
Apache 2.3 came out in 2010 with lot of features in-build.
Official Apache website : http://www.apache.org
Installation guides : http://httpd.apache.org/docs/
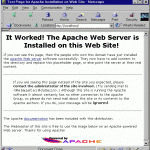
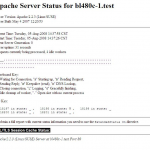
Screen-shots :
- Apache home page
- Apache status page
- Apache logo